Fatigue Testing
Axial Fatigue Testing

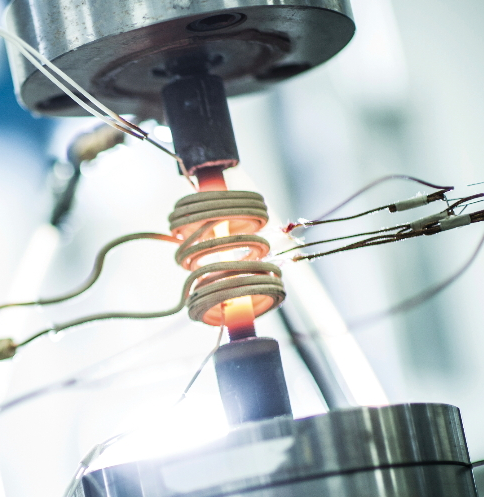
High-temperature Fatigue Testing
Fatigue behaviorscan vary in materials exposed to high temperatures. Cyclic loads applied to materials at elevated temperatures in order to assess performance in harsh environments, long term.
Applications: Aerospace components, exhaust systems, turbine blades.
Key Features: Real-time data collection, testing up to 1,200°C, thermal cycling.
Rotating Beam Fatigue Testing
Ideal for providing insights into a material’s endurance limit, rotating beam fatigue testing is the rotation of specimens under cyclic bending stresses. Shafts and other rotating parts experience forces in real-world applications and durability and safety are critical.
Applications: Rotor components, power transmission, and automotive.
Key Features: Crack propagation monitoring, high-frequency cycling, continuous rotation at various speeds.
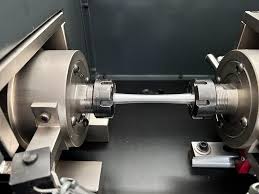

Shear Fatigue Testing
Shear fatigue testing predicts failure points when material’s subject to repeated shear stress and sideways forces.
Applications: Composites, adhesives, bolted connections.
Key Features: Real-time strain data, multi-axis load application, customizable shear angles.
Cryogenic Fatigue Testing
Cryogenic fatigue testing is specifically for materials used in extremely low temperatures to ensure that they perform reliably.
Applications: Cyrogenictanks, spacecraft.
Key Features: Resistance to brittle fracture, temperature-controlled chambers down to -196°C.
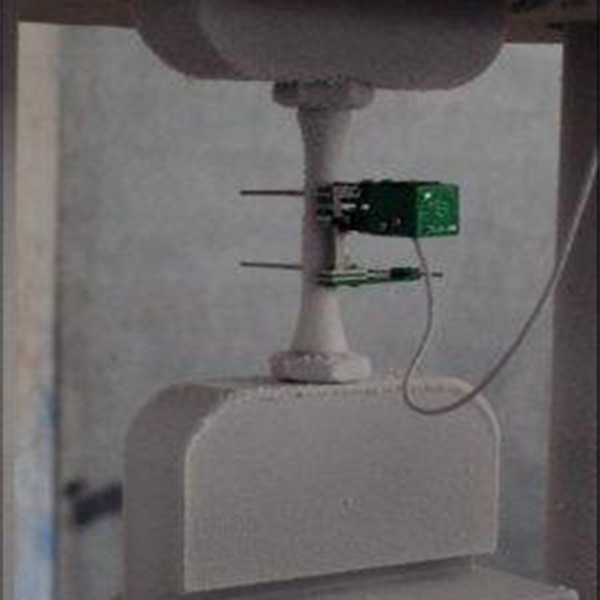

Fatigue strength evaluation of reinforcing bar couplers
Coupleris a mechanical splice used to join two steel reinforcement bars (rebars) in concrete structures. It eliminates the need for lap splicing, saves material, and provides a strong, direct bar-to-bar connection.
Application: Couplers are essential for high-rise buildings, flyovers, bridges, metros, tunnels, and infrastructure projects.
